What Is a Utility Bill and Can It Build Credit?
Published on: 04/09/2023
Utility companies and other essential service providers typically don’t report your utility payments to the credit bureaus. However, some third-party services will report some of those payments, but each third-party service determines exactly what utility bills it will report and which ones it won’t.
A utility bill is a monthly payment due for essential services. Public utilities include electricity, water, and natural gas, waste management, recycling, and wastewater. Although some may not think of them as essential utilities, bills such as landline, cell phone and Internet services are also considered utilities. While streaming services aren’t a utility, some people fold them into that category when organizing bills, especially since some third-party services will report the payments.
Utility companies typically send a monthly bill via email or mail. Depending on the type of utility, you may be charged by usage or with a flat rate fee. In some cases, services may be bundled so that you receive one combined bill, such as water and sewer, where you see each service itemized.
In this guide, we explain if utility bills help build your credit, what types of utility bills you might encounter and what happens if you can’t pay your utility bill.
Does paying your utility bills build credit?
Typically, a utility company does not report your payments to the three major credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion), so your payments — whether on time or late — will not be reflected on your credit report automatically. If you want utility payments to build credit, you can use a third-party service such as Self to report eligible utility bills. Which bills are considered eligible depends on the service you’re using, so compare each third-party service to see which bills it reports.[1]
Types of Utility Bills
While bundling services is common, you may typically receive a bill for each utility that breaks down your utility costs. Each utility and service plan will have a specific breakdown of charges. For most bills, your statement will include basic information, such as your account number, billing period, a total amount, service charges, if applicable, and a due date to pay your bill. This section details your bills and how you might save money on utilities.
Electricity
According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), in 2021 the average electricity bill was $122 per household.[2]
An electricity bill can have a variety of charges, many of which may look different depending on where you live. Your bill may also look different if you’re on a budget billing system — where your usage (measured by kilowatt-hour, abbreviated kWh) for a year is divided by 12 to evenly spread out payments — or a monthly usage system where you are charged for what you use each month. With a monthly usage system, your bill may fluctuate.
Reducing your electricity expense is accomplished by reducing your usage and being more energy-efficient. There are several ways you can do this:[3]
- Unplug unused appliances. Appliances can account for 13% of a home’s energy use.[3] Unplugging unused toasters, coffee makers or blenders can help reduce your energy cost each month.
- Turn off unnecessary lights. Lighting accounts for about 9% of a home’s total energy use. Be conscientious about lights left on needlessly.[3]
- Don’t waste energy unnecessarily. Half-loaded dishwashers, and frequent, high-temperature clothes washing cycles use a lot of energy. Clothing dryers in particular are one of the largest energy users. Be mindful of using more energy than you need and switch to energy-efficient appliances when possible.
Gas
The average U.S. home uses approximately 6 thousand cubic feet (MCF) monthly. One MCF costs an average of $18.72 (as of October 2022), which puts an average monthly gas bill at $1,112 ($18.72 x 6).[4]
Your gas consumption is measured differently depending on where you live. It can be measured in thousands of cubic feet (MCF), hundreds of cubic feet (CCF), or by therm — a measurement equal to 100 CCF.[5]
Homeowners may rely on gas to power ovens, stoves, cooktops, ranges, or furnaces. Depending on your home and service provider, you may receive a gas or a gas bill combined with your electricity bill to cover this utility.
Here are some tips for reducing your monthly gas usage:
- Reduce your heating. If your heat is gas-powered, try lowering your thermostat a small amount or using a space heater instead of heating the whole house.
- Check for air leaks. Check your home for any areas that allow cool air inside, such as windows, external doors, air vents, or power outlets.
- Air dry your clothes. Gas-powered dryers use a lot of fuel. Reduce your gas usage by air drying your clothes instead.
Water and sewage
How much you spend on your water bill depends on your water use, but according to the Environmental Protection Agency, the average family in the U.S. spends $1,100 annually on water costs.[6]
Most water providers will send you a graph showing how much water your household used over a year-long period. Depending on your water service company, this may also include sewer services, which will appear as a sewer charge.
Here are some ways you can reduce your water usage and save money:
- Look for leaks. Dripping faucets and leaking pipes can be costly. Check for these regularly and do any possible repairs.
- Use appliances sparingly. Use energy-efficient appliances, and never run a half-full dishwasher or load of clothes.
- Reconsider your landscaping. Consider an eco-friendlier landscape design, such as a smaller lawn, plants that require less watering, or “hardscape” designs using materials such as stones and boulders.
Trash and recycling
Expenses related to trash disposal and recycling may be bundled into one bill or paid independently — it varies depending on where you live.[7] You may receive a monthly or an annual bill, and costs for trash pickup or recycling collection will also vary depending on the city in which you live.
For example, according to the city of Seattle, Washington, government website, the monthly rate (effective April 2023) to pick up 20 gallons of trash is $32.90.[8]. In Maui, Hawaii, residential service fees are charged annually at $408.[9]
Many of us have become more mindful of how we dispose of our waste for environmental reasons, but there are financial incentives as well. Here are some ways to cut back on your trash waste:
- Try composting. Collect scraps of unused food, such as vegetables or fruits, and use them in your flower beds or backyard as fertilizer. You can collect anything from eggshells to coffee grinds.
- Eliminate single-use plastic. Use a reusable water bottle to carry with you rather than purchase plastic-bottled drinks on the go.
- Opt-in to paperless bills: Instead of having bills and documents sent by mail, sign up for paperless options.
Internet and cable
The average cost for monthly basic internet service at lower download speeds, such as 25 Mbps, in the U.S. is $36.33, and higher speeds cost closer to an average of $58.12.[10] The average cost of a cable television subscription package is approximately $83.[11] Depending on your plan, you may incur additional costs for a wider range of either television or internet services or access.
Here are some ways you can keep your monthly internet and cable bills down:
- Negotiate with your service provider. Always negotiate for a better deal. If there are services bundled in your package that you do not use, see if you can pay less by removing those services or by signing up for a different package. Your provider may have a new promotion you can take advantage of as well.
- Look at what you actually use. Often cable and internet are bundled, but if you primarily use streaming services, you might be able to find a different package that has basic cable and full internet instead of a full cable package that you don’t utilize. The same is true for internet services.
- Shop around. Look for other deals with service providers in your area and see if you can take advantage of a promotional offer or package that best caters to your needs. You can always see if your current provider will match offers from competitors.
Phone
Depending on your cell phone provider and your specific plan, your phone bill vary, but the average price in early 2023 was $144.[12] Your monthly bill can be more or less depending on a number of factors, such as whether you have unlimited service, several lines on one bill, fees specific to your service provider and more.
If you want to reduce your cell phone costs, consider trying these tactics:
- Change service providers. Each service provider has different plans and different deals. Check out the competition and see if you can get a better deal that provides the same coverage and features you currently use.
- Cut back on your services. If you have an unlimited plan, consider basic services instead or at least gauge things like your data usage and slim down a plan tailored to services and usage you actually utilize.
- Join forces. Check out family plans where you can add lines at a discount. You might join a plan your family already has or ask family or friends to join one with you to take advantage of discounted services.
What happens if you can’t pay off your utility bill?
So, what are the consequences if you miss a payment? You may risk late fees or having your services cut off. The laws regarding cutting off utility services for late payment vary state by state. You can find out the laws where you live by visiting your state’s government website.
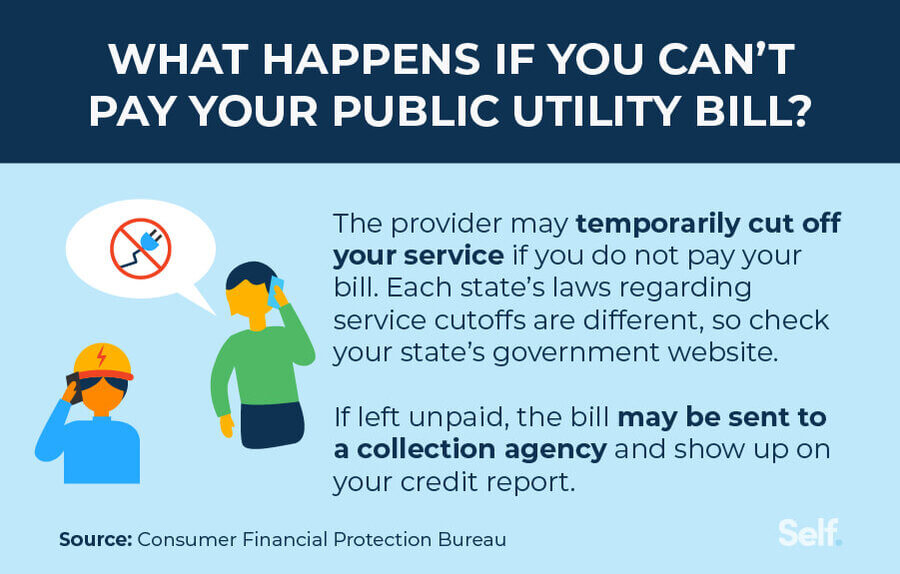
Although missed payments may not be reported to the three major credit reporting bureaus, the bill may be sent to a collections agency if it remains unpaid.[13] Typically, bills get sent to collections after 120 to 180 days of being delinquent. If your utility bill is charged off and sent to collections, it will most likely show up on your credit report.[14]
Should you have difficulty making a payment, you can seek assistance in the following ways:
- The Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP): LIHEAP provides support for lower-income families to meet energy costs.[15]
- Your utility provider: Your utility provider is also a source of assistance. Talk to them about a payment plan or other solution to enable you to pay off your balance without being cut off from your energy source. Some states have protections for certain circumstances, such as no shut offs during winter months. Just make plans to accommodate the bill since you will still owe the money even if your utilities can’t be shut off.
Reviewing your utility bill
Even if your monthly utility expenses are consistent each billing period, it’s a good idea to take some time and learn how to read your monthly utility statements and review them. Doing so gives you a better idea of how much of each service you are using and helps you develop strategies to reduce your utility usage.
Sources
- Experian. “How Utility Bills Can Boost Your Credit Score.” https://www.experian.com/blogs/ask-experian/does-paying-utility-bills-help-your-credit-score/. Accessed January 17, 2023.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. “U.S. residential electricity expenditures increased by $5 per month in 2021.” https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=51958. Accessed January 17, 2023.
- Direct Energy. “What Uses the Most Electricity in My Home?” https://www.directenergy.com/learning-center/what-uses-most-electricity-in-my-home. Accessed January 17, 2023.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. “Natural Gas.”https://www.eia.gov/dnav/ng/NG_PRI_SUM_A_EPG0_PRS_DMCF_M.htm. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Energy Saver. “How to Read Residential Electric and Natural Gas Meters.” https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/how-read-residential-electric-and-natural-gas-meters. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Environmental Protection Agency. “Start Saving.” https://www.epa.gov/watersense/start-saving. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Nationwide. “How much is the average household utility bill?” https://www.nationwide.com/lc/resources/personal-finance/articles/average-cost-of-utilities. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- City of Seattle. “Seattle Public Utilities.” https://www.seattle.gov/utilities/your-services/accounts-and-payments/rates/collection-and-disposal/garbage-rates. Accessed March 17, 2023.
- Country of Maui, Hawaii. “Residential Service Fee & Payment Information.” https://www.mauicounty.gov/1750/Residential-Service-Fee-Payment-Informat. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Forbes. “How Much Does Internet Cost Per Month?” https://www.forbes.com/home-improvement/internet/internet-cost-per-month/. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Cable TV. “How Much Should I Be Paying for Cable TV?” https://www.cabletv.com/blog/how-much-should-i-pay-for-cable-tv. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- CNBC. “Cut your cell phone bill up to 50% with these 4 tips,” https://www.cnbc.com/select/how-to-cut-your-cell-phone-bill-costs/. Accessed March 17, 2023.
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. “Does my history of paying utility bills, like telephone, cable, electricity, or water, go in my credit report?” https://www.consumerfinance.gov/ask-cfpb/does-my-history-of-paying-utility-bills-like-telephone-cable-electricity-or-water-go-in-my-credit-report-en-1817/. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Equifax.” What is a Charge-Off?” https://www.equifax.com/personal/education/credit/report/charge-offs-faq/. Accessed January 18, 2023.
- Office of Community Services. “Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP).”https://www.acf.hhs.gov/ocs/low-income-home-energy-assistance-program-liheap. Accessed January 18, 2023.
About the author
Ana Gonzalez-Ribeiro, MBA, AFC® is an Accredited Financial Counselor® and a Bilingual Personal Finance Writer and Educator dedicated to helping populations that need financial literacy and counseling. Her informative articles have been published in various news outlets and websites including Huffington Post, Fidelity, Fox Business News, MSN and Yahoo Finance. She also founded the personal financial and motivational site www.AcetheJourney.com and translated into Spanish the book, Financial Advice for Blue Collar America by Kathryn B. Hauer, CFP. Ana teaches Spanish or English personal finance courses on behalf of the W!SE (Working In Support of Education) program has taught workshops for nonprofits in NYC.
Editorial policy
Our goal at Self is to provide readers with current and unbiased information on credit, financial health, and related topics. This content is based on research and other related articles from trusted sources. All content at Self is written by experienced contributors in the finance industry and reviewed by an accredited person(s).
